What is a Histogram?
A histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of pixel intensities in an image.
-
X-axis: Represents the range of possible pixel values (e.g., 0-255 for an 8-bit grayscale image).
-
Y-axis: Represents the number of pixels that have a particular intensity value.
Example:
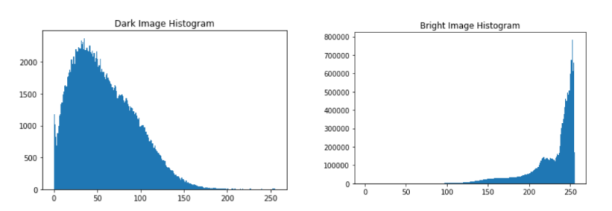
Imagine a grayscale image with mostly dark pixels. Its histogram would show a large peak on the left side (lower intensity values) and fewer bars on the right side (higher intensity values).
Note
- Two Same Image can have same histogram, but Two same Histogram don’t have same image
Properties of Histograms
- Representation of Intensity Distribution: A histogram fundamentally shows the distribution of pixel intensity values within an image. It tells you how many pixels fall within each range of intensity.
- Bins: Histograms divide the range of possible pixel values into intervals called “bins.” The width of these bins can be adjusted, which affects the granularity of the histogram.
- Frequency Count: For each bin, the histogram displays the number of pixels (frequency or count) whose intensity values fall within that bin’s range.
- Shape: The overall shape of the histogram provides valuable information:
- Peaks: Indicate frequently occurring intensity values.
- Valleys: Indicate less frequent intensity values.
- Skewness: A histogram skewed to the left means more dark pixels; skewed to the right means more bright pixels.
- Spread: A wide histogram suggests high contrast, while a narrow one suggests low contrast.
- Normalization: Histograms can be normalized. In a normalized histogram, the sum of all bin values equals 1 (or 100%). This makes it easier to compare histograms of images with different sizes.
- Cumulative Histogram: A cumulative histogram is a variation where each bin’s value represents the cumulative count of pixels up to that intensity level. It’s useful for tasks like histogram equalization.
Histogram Processing
Histogram processing involves modifying the histogram of an image to improve its contrast or enhance certain features. Common techniques include:
-
Histogram Equalization: Stretches the histogram to cover the entire range of possible intensity values, often improving contrast.
-
Histogram Matching (Specification): Transforms the histogram of one image to match the histogram of another image.