Assignment 4: Hands-On SQL Decomposition to 2NF
Scenario:
CREATE TABLE Library (
BookID INT,
ISBN VARCHAR(20),
Title VARCHAR(100),
AuthorName VARCHAR(50),
PublisherName VARCHAR(50),
Price DECIMAL(10, 2),
PRIMARY KEY (BookID)
);1. Functional Dependencies and Partial Dependencies:
-
Functional Dependencies:
BookID→ISBN,Title,AuthorName,PublisherName,Price(BookID determines all other attributes)ISBN→BookID(In this specific example, ISBN could also be considered a determinant as it is stated as the unique identifier for books)
-
Partial Dependencies:
- Since the Primary Key is a single attribute
(BookID), we need to check if other candidate keys exist to identify partial dependencies. - If we consider
ISBNto also be unique for each book, then the following could be considered a partial dependency:Title,AuthorNameare dependent onISBN.
- If we assume multiple books can have the same
AuthorNameorPublisherName, then these can be considered partial dependencies as well:AuthorName→AuthorDetails(If we had more information about the author)PublisherName→PublisherDetails(If we had more information about the publisher)
- Since the Primary Key is a single attribute
2. Decomposition into 2NF:
-
Option 1 (If ISBN is considered a candidate key):
Books(ISBN, Title, AuthorName)Inventory(BookID, ISBN, PublisherName, Price)
-
Option 2 (Considering other potential partial dependencies):
Books(BookID, ISBN, Title, AuthorID, PublisherID, Price)Authors(AuthorID, AuthorName)Publishers(PublisherID, PublisherName)
We will proceed with Option 2 for a more generalized approach.
3. SQL Code to Create New Tables:
CREATE TABLE Authors (
AuthorID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
AuthorName VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE Publishers (
PublisherID INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
PublisherName VARCHAR(50)
);
CREATE TABLE Books (
BookID INT PRIMARY KEY,
ISBN VARCHAR(20),
Title VARCHAR(100),
AuthorID INT,
PublisherID INT,
Price DECIMAL(10, 2),
FOREIGN KEY (AuthorID) REFERENCES Authors(AuthorID),
FOREIGN KEY (PublisherID) REFERENCES Publishers(PublisherID)
);4. SQL INSERT Statements:
INSERT INTO Authors (AuthorName) VALUES
('J.K. Rowling'),
('Stephen King');
INSERT INTO Publishers (PublisherName) VALUES
('Bloomsbury'),
('Scribner');
INSERT INTO Books (BookID, ISBN, Title, AuthorID, PublisherID, Price) VALUES
(1, '978-0747532743', 'Harry Potter and the Philosopher''s Stone', 1, 1, 10.99),
(2, '978-0451169518', 'The Shining', 2, 2, 8.99);5. Querying the Normalized Schema:
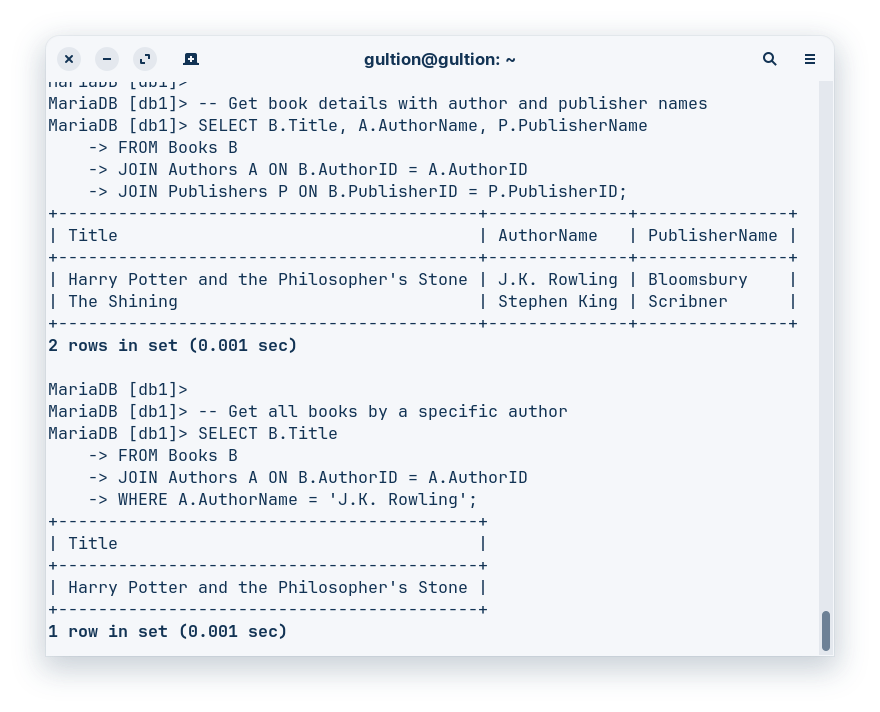
-- Get book details with author and publisher names
SELECT B.Title, A.AuthorName, P.PublisherName
FROM Books B
JOIN Authors A ON B.AuthorID = A.AuthorID
JOIN Publishers P ON B.PublisherID = P.PublisherID;
-- Get all books by a specific author
SELECT B.Title
FROM Books B
JOIN Authors A ON B.AuthorID = A.AuthorID
WHERE A.AuthorName = 'J.K. Rowling';