Assignment 1: SQL-Based Conversion from 3NF to 2NF
Scenario:
CREATE TABLE Employee_Courses (
EmpID INT,
CourseID INT,
EmpName VARCHAR(50),
CourseName VARCHAR(50),
InstructorName VARCHAR(50),
PRIMARY KEY (EmpID, CourseID)
);1. Functional Dependencies and Partial Dependencies:
- Functional Dependencies:
EmpID→EmpName(Employee ID determines Employee Name)CourseID→CourseName,InstructorName(Course ID determines Course Name and Instructor Name)EmpID,CourseID→EmpName,CourseName,InstructorName(The combination of Employee ID and Course ID determines all other attributes)
- Partial Dependencies:
EmpNameis dependent only onEmpID(part of the primary key).CourseNameandInstructorNameare dependent only onCourseID(part of the primary key).
2. Why This Table is in 3NF but Violates 2NF:
- 3NF: The table is in 3NF because there are no transitive dependencies (no non-prime attribute is dependent on another non-prime attribute).
- 2NF Violation: The table violates 2NF because it has partial dependencies. 2NF requires that every non-prime attribute be fully functionally dependent on the entire primary key, not just a part of it.
3. Decomposition into 2NF:
To achieve 2NF, we need to decompose the table into smaller tables, eliminating the partial dependencies.
4. SQL Commands to Create Decomposed Tables:
-- Table for Employee information
CREATE TABLE Employees (
EmpID INT PRIMARY KEY,
EmpName VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Table for Course information
CREATE TABLE Courses (
CourseID INT PRIMARY KEY,
CourseName VARCHAR(50),
InstructorName VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Table for linking Employees and Courses
CREATE TABLE EmployeeCourses (
EmpID INT,
CourseID INT,
PRIMARY KEY (EmpID, CourseID),
FOREIGN KEY (EmpID) REFERENCES Employees(EmpID),
FOREIGN KEY (CourseID) REFERENCES Courses(CourseID)
);5. SQL Commands to Insert Data:
-- Insert data into Employees
INSERT INTO Employees (EmpID, EmpName) VALUES
(1, 'Alice'),
(2, 'Bob'),
(3, 'Charlie');
-- Insert data into Courses
INSERT INTO Courses (CourseID, CourseName, InstructorName) VALUES
(101, 'Database Management', 'Dr. Smith'),
(102, 'Web Development', 'Prof. Johnson'),
(103, 'Data Structures', 'Dr. Williams');
-- Insert data into EmployeeCourses
INSERT INTO EmployeeCourses (EmpID, CourseID) VALUES
(1, 101),
(1, 102),
(2, 101),
(3, 103);6. SQL Commands to Query Data:
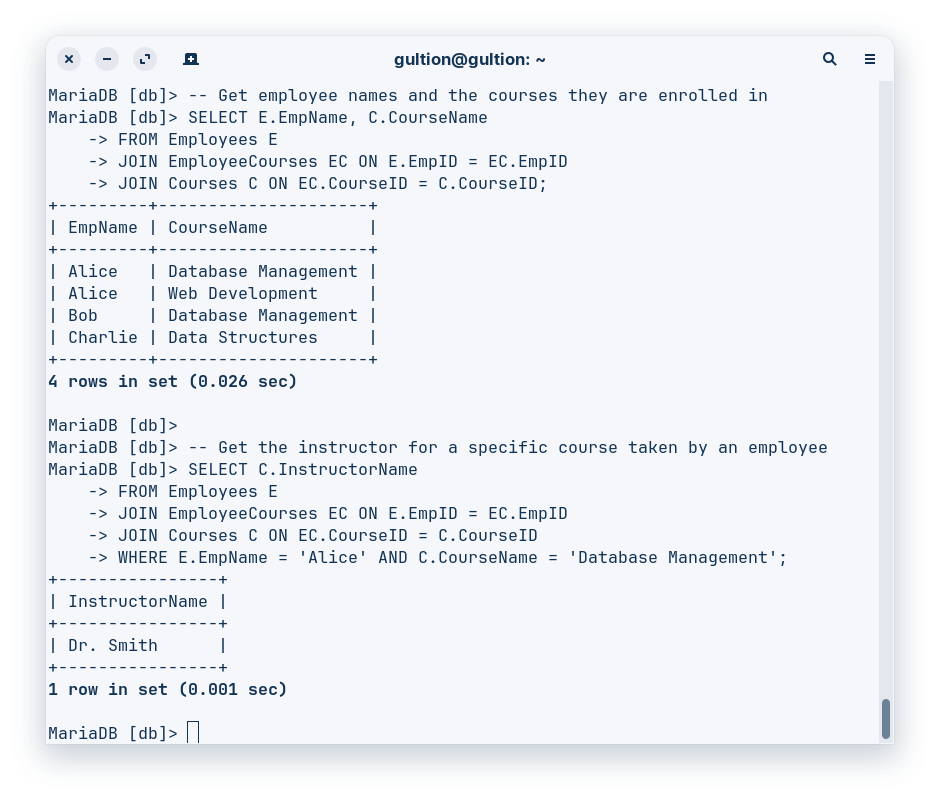
-- Get employee names and the courses they are enrolled in
SELECT E.EmpName, C.CourseName
FROM Employees E
JOIN EmployeeCourses EC ON E.EmpID = EC.EmpID
JOIN Courses C ON EC.CourseID = C.CourseID;
-- Get the instructor for a specific course taken by an employee
SELECT C.InstructorName
FROM Employees E
JOIN EmployeeCourses EC ON E.EmpID = EC.EmpID
JOIN Courses C ON EC.CourseID = C.CourseID
WHERE E.EmpName = 'Alice' AND C.CourseName = 'Database Management';